My Research Fields
- Polar Ring Galaxies
- Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies
- Star Formation Histories
- Sinology
- Long-slit spectroscopy
- Integral Field Spectroscopy
- Color Magnitude Diagrams
- Cultural musicology
Sonification
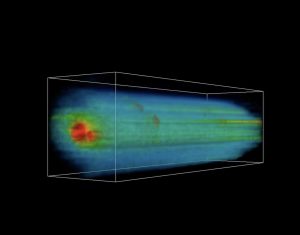 Sonification offers an alternative pathway for exploring data by translating quantitative information into sound. This technique provides an intuitive means of identifying structures, trends, and anomalies that may be difficult to discern visually or whose interpretation may benefit from multimodal approaches.
Sonification offers an alternative pathway for exploring data by translating quantitative information into sound. This technique provides an intuitive means of identifying structures, trends, and anomalies that may be difficult to discern visually or whose interpretation may benefit from multimodal approaches.
For example, I have applied sonification to spectroscopic and integral-field datasets to facilitate the exploration of complex datacubes. This method has also proven effective for communicating astronomical results to broader audiences, making the underlying physical processes more accessible and inclusive.
HII Regions
HII regions are important star formation tracers in the chemical evolution of galaxies and can be used as standard candles to estimate cosmological distances. Equally important, they are the best indicators of the conditions that lead to massive star formation
Gaseous Nebulae
 Emission lines allows to study the realm of gaseous nebulae, its physical properties and chemical composition.
Emission lines allows to study the realm of gaseous nebulae, its physical properties and chemical composition.
Hot stars in young star forming regions create beautiful spectra full of spiky lines.
On the other hand, some dying stars create amazing expanding shells of luminous gas. In recent works I have been using Planetary nebulae as tracers for studying the chemistry, kinematics, and stellar contents of M31 substructures. They are also one of the best candidates that can provide both very accurate velocities and precision abundance measurements of elements such as O, He, Ne, N, Ar, and S.
Star Formation

Star formation is an ongoing process in the local universe. Most of the light and metals are produced in the most massive among the newly formed stars. The most extreme regions forming massive stars are often referred to as starbursts. In the local universe they account for about a quarter of all star formation, and this fraction may be larger in the younger universe.
GalaxyFormationEvolution
 Galaxies are a complex mix of stars, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter, distributed in the bulge, disk, and halo. The present day structure and dynamics of these galaxy sub-components are intimately linked to their assembly and evolution over the age of the Universe.
Galaxies are a complex mix of stars, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter, distributed in the bulge, disk, and halo. The present day structure and dynamics of these galaxy sub-components are intimately linked to their assembly and evolution over the age of the Universe.
During the past recent years I have been working in a project to establish observational constraints to models of galaxy formation and evolution, by resolving in time and space the properties of the stellar populations of galaxies in the local Universe, using state-of-the art data from the CALIFA survey.